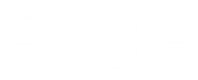Covalent bonds in a giant lattice are broken. Metals also have a giant chemical structure whether the metal is pure or an alloy.
Giant Covalent Structures C2 4 Teaching Resources

Is Diamond A Giant Covalent Structure Seniorcare2share

Giant Covalent Structures Aqa Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes
This is an example of a covalent bond which is created because of the higher electronegativity of oxygen.

Giant covalent structures. Covers basic atomic properties electronic structures ionisation energies electron affinities atomic and ionic radii and the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum bonding including intermolecular bonding and structures ionic molecular giant covalent and metallic. Covalent bonding is the type of bond that holds together the atoms within a polyatomic ion. Have giant covalent structures 1 ii Which one of the following questions cannot be answered by science alone.
Valence only describes connectivity it does not describe the geometry of molecular compounds or what are now known to be ionic compounds or giant covalent structures. The greater the difference the stronger the attraction between the positive ion cation and negative ion anion. Ionic compounds contain ionic bonds.
The giant covalent structure of diamond. Atoms can sometimes be forgotten in structures when assumed to be there. Simple molecular substances and giant covalent structures have different properties.
Shared pair of electrons Macromolecular. Should iodine be added to salt in food. What harm does a lack of iodine do.
They change their structures from ionic to covalent as their solids transition to liquids or vapors. In a macromolecule all the atoms are bonded to each other by covalent bonds in a giant lattice structure. Contains a huge number of atoms or ions arranged in a particular way but the number of particles is not fixed the ratio might be fixed but not in all cases.
Aluminum chloride and phosphorusV chloride are more complicated. Figure shows the structures of diamond and silicon dioxide. These macromolecules a have high melting and boiling points because a lot of heat energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds in the giant lattice structure.
Network covalent structures or giant covalent structures contain large numbers of atoms linked in sheets such as graphite or 3-dimensional structures such as diamond and quartz. Giant covalent substances have many atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Electrostatic force of attraction between the metal positive ions and the delocalised electrons Magnesium Sodium all metals Only use the words molecules and intermolecular forces when talking about simple.
Electrostatic forces of attraction between ions are overcome. Simplifies large structures to highlight important atoms bonds and groups. Carbon has an electronic arrangement of.
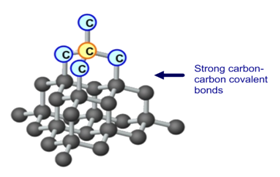
It takes two electrons to make a covalent bond one from each bonding atom. Electrons are borrowed from these other carbon atoms. A diamond has a giant molecular structure.
Electronegativity values of course. Tick one box. Covalent compounds also are known as molecular compounds.
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms. Molecules are separated into ions. Many compounds in the world are formed by ionic bonds and are therefore ionic compounds.
In quantum physics organic chemistry and biochemistry the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. Giant structure occurs in ionic and covalent compounds. This is possible due to the presence of shared electrons.
Shows three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and bonds. Basically we can divide chemical structures into two types. A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
1 Metals contain a lattice of negative ions in a sea of electrons. Diamond graphite and graphene are forms of carbon with different giant covalent structures. Sodium chloride and magnesium chloride are ionic and consist of large ionic lattices at room temperature.
Substances with small molecules have low melting and boiling points and. These substances have high melting and boiling points are frequently brittle and tend to have high electrical resistivity. An ionic bond is formed when there is a large electronegativity difference between the elements participating in the bond.
A diamond is an example of Giant Covalent bond of carbon. The structure of diamond. Explain the differences between ionic and covalent bonds and ionic and covalent compounds.
Identification of atoms requires a key of color representations. These giant molecular structures are basically lattices made up of molecules which are held together by covalent bonds structure. Lets go through each.
These covalent bonds are very strong. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge. The line between atoms does not represent a pair of electrons as it does in Lewis diagrams.
This module explores two common types of chemical bonds. The millions of different chemical compounds that make up everything on Earth are composed of 118 elements that bond together in different ways. This page describes the structures of giant covalent substances like diamond graphite and silicon dioxide siliconIV oxide and relates those structures to the physical properties of the substances.
Lewis dot structures are one way to represent how atoms form covalent bonds. They form huge structures where a huge number of atoms are held together. The module presents chemical bonding on a sliding scale from pure covalent to pure ionic depending on differences in the electronegativity of the bonding atoms.
Diamond Graphite Silicon dioxide Silicon Metallic. In the kinetic theory of gases the term molecule is often used. What dictates which kind of bond will form.
How much sodium chloride is in food. Covalent bonding results in the formation of molecules or giant structures. Electrons are released from atoms.
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Below are two statements about metals. Covalent bonding generally happens between nonmetals.
Ionic Bond Covalent Bond James Bond so many bonds. This is discussed in greater detail below.

Giant Covalent Structures Flashcards

Giant Molecular Structure Diamond Graphite O Level Chemistry Notes

Giant Covalent Macromolecules Secondary Science 4 All

Giant Covalent Structures Flashcards Quizlet
Giant Covalent And Simple Molecular The Student Room

Giant Covalent Compound Properties Ppt Video Online Download
1 49 Explain Why Substances With Giant Covalent Structures Are Solids With High Melting And Boiling Points Tutormyself Chemistry
Igcse Chemistry 2017 1 49 Explain Why Substances With Giant Covalent Structures Are Solids With High Melting And Boiling Points